The other day I noticed a very interesting photo on a fellow Australian ham blogger, Peter Mark’s site. The blog entry was titled a “Radio nerd’s tour of Canberra“. The first photo is described as ‘a transceiver with a nifty antenna tuner’. But the instant I saw it I sensed there was slightly more to it.
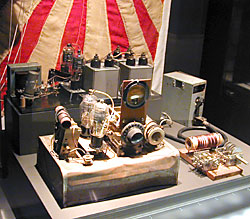
The fact that it was built on a beaten up old kerosene can prompted me to google “Winnie the war winner” and the results confirmed Peter’s photo is of this most famous piece of Australian ham homebrew ingenuity. Max (Joe) Loveless’ skill to be precise. The photo prompted me to find out the story of this iconic wireless set that’s an inspiration to a generation of Australian radio hams proud of their traditions of ‘making-do’.
The wikipedia entry on the Battle of Timor gives detailed historical and military background to this little radio’s moment of fame in April 1942.
As a result of British intrigue Australian troops were sent to Portuguese East Timor to disrupt any Japanese invasion on Australia’s northern doorstep. By April the 2/2nd Independent Company had been fighting a guerilla campaign for four months. Many were ill and they were low on supplies, and had had no contact with Australia since February.
For weeks a team had been trying to build a transmitter from salvaged parts from damaged radio gear. Before the war Max Loveless was a radio amateur in Hobart with the call 7ML. He became a Signaller with “Sparrowforce” on the Dutch part of Timor with the Australian Infantry Forces (AIF).

Bill Marien reported the story in the Melbourne Argus of 1st January 1943:
“Force Intact. Still Fighting. Badly Need Boots, Money, Quinine, Tommygun, Ammunition.”
This was the first official message received in Australia from the lost AIF commandos of Portuguese Timor who, for 59 days after the Japanese landing on the island, had been written off as missing or dead.
The signal came to Darwin on the night of April 19. It was transmitted by “Winnie the War Winner,” a crazy contraption built from scraps of wire and tin, and pieces of long discarded radio sets.
When the commandos showed me the incredible Winnie recently, it was easy to recapture the scene of that night of April 19.
In the thin air of a Timor mountain hideout, 4 bearded, haggard Australians were working by the smoking, stinking light of a pig-fat flare. Three of them watched anxiously as the fourth thumbed a Morse key. Weak batteries sent the dots and dashes of the morse dimly across the Arafura Sea to the Northern Territory of Australia. The tension was something physical as the operator strained his ears for a reply. At last a reply came.”
The AIF commando force which had been in Portuguese Timor were joined by other Australians from Dutch Timor including two signalmen, Cpl John Sargeant, of Bonshaw, NSW, and Lance-Cpl John Donovan, of Lindfield, NSW. Under leadership of Capt George Parker, of Earlwood, NSW, they joined Sigs Max (Joe) Loveless, of Hobart, and K. Richards, of Victoria, both of the original commando force.
“On March 8 the 4 men got to work — Loveless just out of sick bed and Sargeant just recovered from malaria. Three days later a Dutch sergeant, exhausted, stumbled in. He had carried what he thought to be a transmitter-receiver 40 miles through some of the roughest country in the world. It was an ordinary commercial medium-wave receiving set – and out of order.
CORPORAL WENT SCROUNGING
Loveless, whose knowledge made him No 1 man of the team, thought he could build a one-valve transmitter from parts of this set and of another small and weak set. He planned a circuit, and all the commandos were asked to be on the lookout for anything that might serve as a radio part.
Cpl Donovan went scrounging at Attamboa, on the north coast, to see what he could salvage, while his companions recovered an abandoned army set. The parts of the 3 sets were unsoldered, and a bamboo used to catch all the melted solder for re-use. Loveless had carefully preserved 2 small batteries, but they needed recharging. A generator was taken from an abandoned 10-year old car and rigged to a series of wooden wheels, which a native was persuaded to turn. The set was complete on March 26.
It would not work!

The only tools available were a tomahawk, pliers, and screw-driver. They had no test equipment to determine the set’s frequency. The coils were wound on pieces of bamboo.
On March 28 Donovan returned from Attamboa – laden like a treasure ship. He had the power pack from a Dutch transmitter, 2 aerial tuning condensers, 60ft of aerial wire in short lengths, and a receiving set. Next day the men had to move all their precious gear, for the Japanese were getting too close.
Loveless got to work on a second transmitter twice as big as the first, and built it into a 4-gallon kerosene tin. A battery charger was recovered from enemy-held territory. To get it 14 commandos went through the Japanese lines to the old Australian headquarters at Villa Maria. There, within 100 yards of Japanese sentries, protected only by the dark, they dug up the charger which had been buried when the headquarters were evacuated.
HEARD DARWIN WAS SAFE
On April 10 the signallers heard Darwin on the receiver, and knew then that Darwin was still in Australian hands. But their second transmitter was also a failure.
Loveless had another idea, but he needed more batteries. Four were found. Then the petrol ran out and the charger could not be kept running. So they raided the Japanese lines and carried off tins of kerosene. Finally the charger was started on kerosene and run on diesel oil.
With batteries at full strength they signalled Darwin on April 18, but got no reply. They did not know that their message had been picked up on the Australian mainland and passed on to Darwin, that all transmitting stations had been warned to keep off the air and listen to Timor the following night.
You can get a good sense of the story from this video of the documentary ‘The Men of Timor’ filmed in Timor by Damien Parer in late September 1943. You can see a reconstruction of the building of the radio about 3’16″ in from the start.
On the 19th April they heard Darwin but their batteries failed again.
On the night of April 20 they again got Darwin. But Darwin was suspicious; demanded proof of their identity. So questions and answers like these were rushed across the Arafura Sea:
“Do you know Bill Jones?”— “Yes, he’s with us.”
“What rank, and answer immediately?”— “Captain.”
“Is he there? Bring him to the transmitter. . . . What’s your wife’s name, Bill?”— “Joan.”
“What’s the street number of your home?”
Once they provided the correct answers, help was on its way.
I found the newspaper report on the National Library of Australia’s brilliant Trove, where digital versions of many Australian newspapers have been put online courtesy of crowd-sourced editors across the global internet. Truly astounding!
Leave a Reply